From Raw Data to Profitable Insights: Tools and Strategies for Successful Data Monetization
Data monetization has become an increasingly important topic in the world of business and technology. As companies collect more and more data, they are realizing the potential value that this data holds. In fact, according to a report by 451 Research, the global market for data monetization is projected to reach $7.3 billion by 2022. This is achieved through various strategies such as selling raw or processed data, providing analytics services, or creating new products based on the data.
There are many different approaches to data monetization, each with its own unique benefits and challenges. However, many organizations struggle with how to effectively monetize their data assets. In order to effectively monetize data, businesses need the right tools and strategies in place. These tools help collect, analyze, and visualize data to uncover valuable insights that can be turned into profitable opportunities. Below is a short list of essential tools used for successful data monetization.
- Data Collection Tools: The first step in data monetization is collecting relevant and accurate data. This requires efficient and effective data collection tools such as web scraping software, API integrations, IoT sensors, and customer feedback forms. These tools help gather large amounts of structured and unstructured data from various sources like websites, social media platforms, customer interactions, or even physical sensors.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Analytics tools play a crucial role in making sense of complex datasets by identifying patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed. By leveraging these platforms, businesses can gain valuable insights that can be used for decision-making processes. They provide powerful reporting dashboards that allow businesses to visualize their KPIs with interactive charts, graphs, or maps helping them understand how their products are performing in real-time.
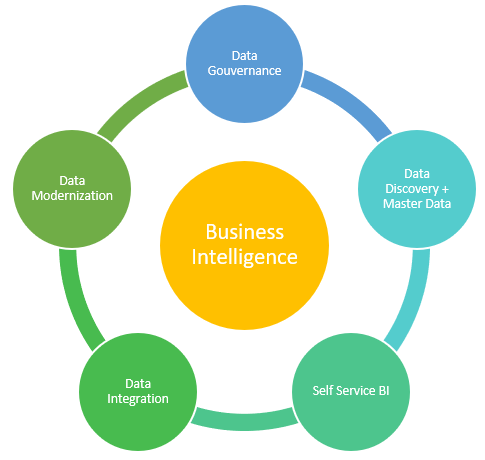
- Business Intelligence Tools: These are applications designed specifically for reporting and dashboarding purposes. They allow users to input raw or analyzed data from various sources and present it in a visually appealing manner through charts, graphs or maps.
- Customer Relationship Management Systems: CRM systems are essential tools for gathering customer-related information such as demographics, purchase history or behavior patterns. By analyzing this data, businesses can better understand their customers and tailor their products or services to meet their specific needs.
- Data Management Platforms: DMPs are software solutions that help businesses to store, and manage large volumes of data from different sources. They allow for the integration of various data types, such as first-party and third-party data, which can then be used to create targeted marketing campaigns. It also provides features such as real-time processing capabilities, automated workflows for cleansing and transforming data, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Data Visualization Tools: Data visualization tools help businesses present data in a compelling and visually appealing manner, making it easier for decision-makers to understand complex information quickly. These tools provide interactive dashboards, charts, maps, and graphs that can be customized according to the needs of the business.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: AI & ML technologies can help organizations extract valuable insights from their data by identifying patterns, predicting trends, and automating processes. AI-powered chatbots also enable businesses to engage with customers in real-time, providing personalized recommendations and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing provides scalable storage and computing power necessary for processing large amounts of data quickly. It also offers cost-effective solutions for storing and managing data as businesses can pay only for the services they use while avoiding expensive infrastructure costs.
- Demand-side platforms: DSP help organizations manage their digital advertising campaigns by targeting specific audiences based on their browsing behavior or interests. These platforms allow businesses to use their data to segment and target customers with personalized messaging, increasing the chances of conversion and revenue generation.
- Monetization Platforms: Finally, businesses need a reliable monetization platform that helps them package and sell their data products to interested buyers easily.
Data is certainly more than you think! It’s a valuable resource that can be monetized across your organization. So get in touch with us and learn how data monetization can transform your business.