Cloud Computing: A Life-Saver for Businesses in Crisis Situations
In times of crisis, businesses need reliable solutions to keep their operations running smoothly. From natural disasters to pandemics, the right digital infrastructure can make a world of difference in terms of both cost and efficiency. That’s why more and more companies are turning to cloud computing – a digital solution that promises maximum data security while being highly scalable and cost-effective.
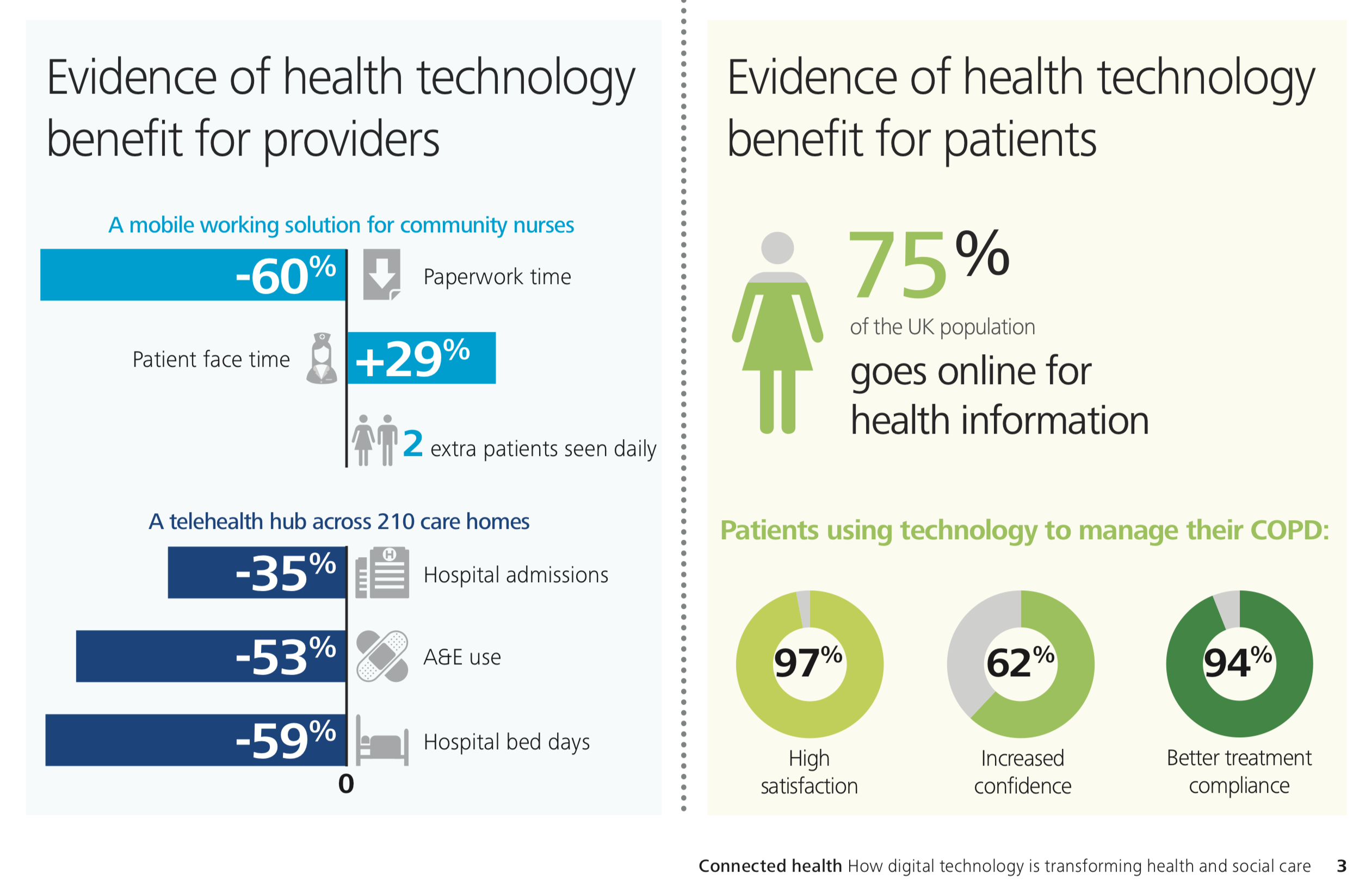
It’s proven that Cloud computing is a life-saver for businesses in crisis situations. It allows businesses to continue operating even when faced with power outages, natural disasters, and other unexpected events. By storing data and applications in the cloud, businesses can keep their critical operations running and avoid costly downtime.
The benefits of cloud computing for businesses in crisis situations include:
- Increased Flexibility: Cloud computing gives businesses the ability to scale up or down as needed, which can be a lifesaver during times of crisis when demand is unpredictable.
- Reduced Costs: The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing can help businesses save money during times of crisis when every penny counts.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The collaborative features of many cloud-based applications can help businesses stay connected and work together effectively even when employees are working remotely.
- Improved Disaster Recovery: With cloud backup and disaster recovery solutions, businesses can protect their critical data and systems from being lost or damaged in the event of a disaster.
- Greater agility: In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to quickly adapt to change is critical for survival. Cloud computing gives businesses the agility they need to make changes on the fly and keep up with the competition.
How Does Cloud Computing Help with Business Continuity?
Business continuity is an important consideration for any business, and cloud computing can be a valuable tool in maintaining business continuity. Cloud computing can provide businesses with the ability to maintain access to their data and applications in any given circumstance. Additionally, cloud computing can provide businesses with the ability to scale their resources up or down as needed, which can help to ensure that they have the resources they need during times of increased demand.
There are many different cloud computing solutions available, and the best one for your business will depend on your specific needs. However, there are some general best practices that you should follow when implementing a cloud solution:
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Solutions
There are many different cloud computing solutions available, and the best one for your business will depend on your specific needs.
However, there are some general best practices that you should follow when implementing a cloud solution:
-
- Define Your Goals: Before you even start looking at different cloud solutions, you need to take a step back and define what exactly you want to achieve with the move to the cloud. What are your specific goals and objectives? Once you have a clear understanding of what you want to achieve, you can start evaluating different options to see which one is the best fit for your business.
- Do Your Research: Don’t just go with the first cloud solution that you come across. Do your research and compare different options before deciding. Consider factors such as pricing, features, scalability, security, and support when making your decision.
- Work with a Reputable Provider: When it comes to choosing a cloud provider, it’s important to work with a reputable and experienced company. Choose a provider that has a good track record and is able to meet your specific needs. Ask for references from other businesses that have used the provider’s services before making your final decision.
- Implement a Pilot Program First: Before moving all of your data and applications to the cloud, it’s often helpful to implement a pilot program first. This will allow you to test out the cloud solution and make sure that it works well for your business. It’s also a good way to get a feel for the provider’s customer service and support.
- Stay Up to Date: Cloud technology is constantly evolving, so it’s important to stay on top of the latest trends and changes. Make sure that your cloud solution is up to date with the latest features and security measures in order to ensure that you’re getting the most out of your investment.
Following these best practices will help ensure that your cloud solution is implemented successfully and meets your business needs.
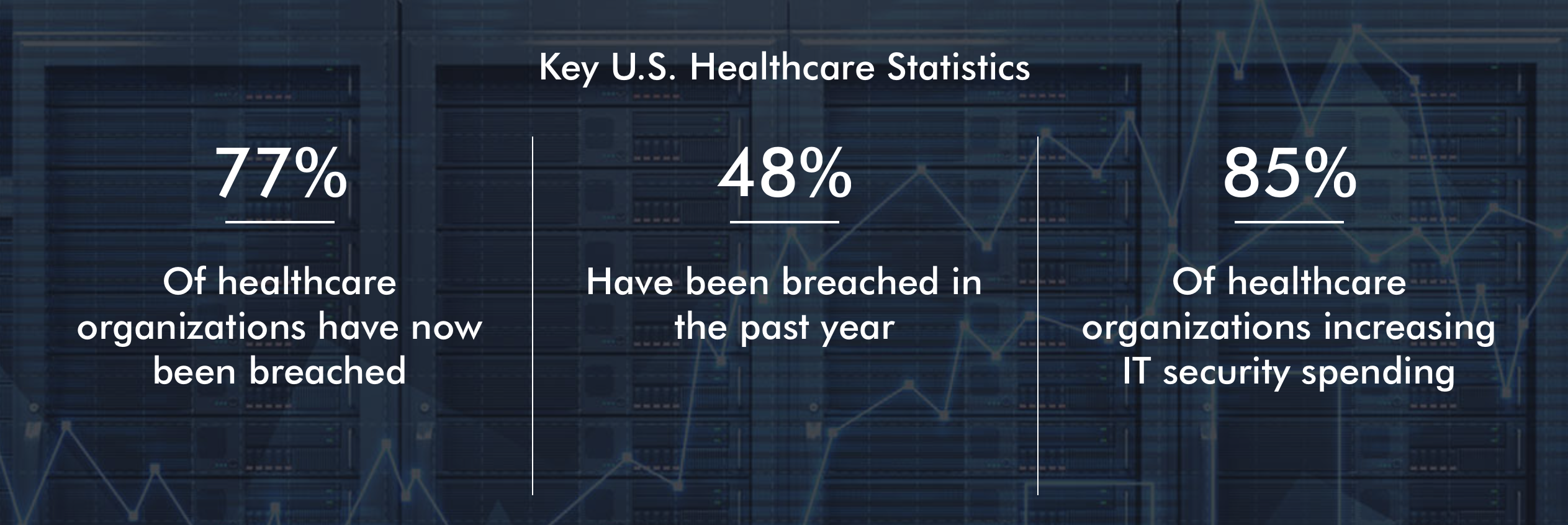
Nevertheless, there are a few critical considerations to take into account when choosing a cloud provider, particularly for businesses in crisis situations. The 1st is scalability: can the provider scale up or down to meet the changing needs of the business? 2nd is reliability: is the provider’s infrastructure reliable and robust enough to handle mission-critical workloads? 3rd is security: how well does the provider protect data and ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations? 4th is cost: what is the total cost of ownership for using the provider’s services? And lastly, flexibility: how easy is it to use the provider’s services and how much control does the customer have over their own data and applications?
To choose the best possible cloud provider for your business, it’s important to understand your own requirements and objectives so you can evaluate different providers to see which one best meets your needs.
At Xorlogics, we advise you on all questions regarding the introduction, update or optimization, maintenance, and further development of your IT systems according to your needs and are at your side as a competent partner. We are happy to assist you in all technical areas. Thanks to our many years of experience, we know what is important, and which hardware and software make sense for your work processes. Just contact us and we will be happy to advise you.